A Third Grade Teacher Is Creating a Language Arts Lesson to Address the Following Standard
Preparation Manual
![]()
Department four: Sample Selected-Response Questions
Bilingual Education Supplemental (164)
Expand All Answers | Collapse All Answers
This section presents some sample exam questions for yous to review as part of your preparation for the exam. To demonstrate how each competency may be assessed, sample questions are accompanied past the competency that they measure. While studying, you may wish to read the competency before and after you consider each sample question. Please note that the competency statements practise non appear on the actual test.
For each sample test question, there is a correct reply and a rationale for each answer pick. The sample questions are included to illustrate the formats and types of questions you will come across on the test; however, your performance on the sample questions should non be viewed as a predictor of your performance on the actual examination.
Domain I—Bilingual Education
Competency 001—The beginning Bilingual Education teacher understands the foundations of Bilingual Educational activity and the concepts of bilingualism and biculturalism and applies this knowledge to create an effective learning environment for students in the Bilingual Education program.
one. The process in which members of dissimilar cultural groups within the same society reciprocally prefer and appreciate the attitudes, values, and language patterns of each other is known equally
- assimilation.
- acculturation.
- transculturation.
- ethnoconvergence.
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Respond expanded
- Choice B is right because acculturation involves mutual respect and interchange amongst groups. Choice A is incorrect because assimilation involves the minority group giving upwardly their values and language to adopt those of the bulk group. Pick C is wrong considering transculturation involves pocket-sized scale adoption of cultural values with very trivial visible touch. Selection D is incorrect because ethnoconvergence involves people self-dividing themselves into smaller ethnic groups within a "superethnicity" such as a nationality.
2. The bilingual instruction director for a school district meets with all the bilingual teachers and suggests that didactics should exist interactive, student-centered, and anchored on the language and culture of the students' domicile. Which of the following is the all-time rationale for the blazon of educational activity described?
- Relating instruction to the students' cultural backgrounds promotes academic success
- Cooperative learning improves students' cognitive, academic, social, and affective growth
- Instruction that promotes multicultural awareness develops students' cross-cultural competency
- Creating opportunities for students to receive instruction from fluent speakers of both students' native language and English is straight related to student success
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Respond expanded
- Option A is correct considering the strategies described appropriately relate instruction to the students' cultural background, including their native language, which volition promote academic success. Option B is incorrect because the strategies promoted by the director practice not involve cooperative learning. Option C is incorrect because to promote cantankerous-cultural competency, educational activity should include cultures represented outside of the class. Selection D is incorrect because, in the scenario presented, fluent speakers of L1 and L2 are not providing instruction.
iii. Given that English-language learners (ELLs) often differ in their culture and degree of English-linguistic communication proficiency, which of the following types of program models would best ensure their bookish success?
- Programs that concentrate on English as a second linguistic communication (ESL) instruction with an emphasis on the ELLs' quick assimilation into the school culture
- Programs that mainstream ELLs fully into grade-level classrooms in which the curricular standards are modified to their achievement level
- Programs that address the ELLs' needs by using a standards-based program in which content is taught in a comprehensible style
- Programs that are individualized to each ELL's needs
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Pick C is right considering the nigh advisable manner to address the needs of ELLs is to use a standards-based program that makes content-based pedagogy comprehensible to them. Option A is incorrect because quick assimilation into the school culture volition not ensure academic success. Option B is incorrect considering the curricular standards should not be modified for ELLs; merely instruction should be modified to adjust their needs. Option D is incorrect because programme models are not modified for individual ELLs; just instruction is modified.
four. In which of the following court cases did the United States Supreme Court rule that limited-English-skillful students should receive equal admission to didactics under the Ceremonious Rights Act?
- Castañeda v. Pickard
- Meyer v. Nebraska
- Lau v. Nichols
- Plyler v. Doe
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Choice C is correct because Lau v. Nichols adamant that identical education does not constitute equal teaching under the Civil Rights Act by "but providing students with the aforementioned facilities, textbooks, teacher and curriculum; for students who practise not understand English are effectively foreclosed from any meaningful education." Pick A is incorrect because Castañeda five. Pickard determined the criteria schools should use to educate students with limited English proficiency. Pick B is incorrect because Meyer v. Nebraska overturned the 1919 Nebraska statute claiming that "no person, individually or every bit a teacher, shall, in any individual denominational, parochial or public school teach any subject area to whatsoever person in any language." Option D is wrong because in Plyler v. Doe, the court ruled that children could not be denied an didactics based on immigration status.
v. Which of the post-obit statements provides the all-time explanation for the improved academic performance that English-language learners (ELLs) feel in an additive educational program?
- The apply of English (L2) as conversational language is enforced in order to larn L2 academic language
- The exclusive use of primary language (L1) for language-arts didactics and L2 for other content instruction helps ELLs develop bilingual skills while avoiding language confusion
- The dual-language environment requires ELLs to develop stronger study skills than their peers require in monolingual L2 classes
- The continued development of ELLs' L1 validates their L1 cognition and facilitates the acquisition of their L2
- Enter to aggrandize or plummet answer. Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because condiment education includes continuing to build ELLs' L1, hence facilitating the acquisition of their L2. Option A is wrong because, while L2 conversational language is important, L2 is not the focus in an additive educational program. Pick B is incorrect considering additive educational programs apply L1 beyond content-surface area instruction. Option C is incorrect considering a student's study skills do not influence the effectiveness of an additive educational program.
6. Which of the following strategies would exist nigh effective in creating an environment that encourages the development of biliteracy and biculturalism?
- Incorporating materials related to students' dwelling house cultures and texts in students' primary language throughout the curriculum
- Edifice opportunities for English language and literacy evolution across all content curriculum
- Hosting food and clothing days that feature the home cultures of students in a grade and encouraging the students' parents to participate
- Decorating the classroom with student drawings based on stories from students' home cultures and English
- Enter to expand or collapse respond. Answer expanded
- Option D is correct considering decorating the classroom with such drawings promotes biliteracy and biculturalism by incorporating both L1 and L2 literacy materials and celebrations of students' personal reflections of their habitation cultures. Option A is incorrect because incorporating texts in students' main language and cultures just promotes first language development. Pick B is incorrect because the edifice opportunities are merely for English language evolution. Option C is wrong because while the events encourage culture, they lack a literacy focus.
seven. An administrator wants English language-language learners (ELLs) to take standardized accomplishment tests of basic reading skills that have been directly translated from English into the ELLs' native languages. Which of the post-obit best explains why that approach is probable to yield inaccurate results?
- A translated examination will accept slightly increased levels of validity and reliability simply volition not reduce student exam feet
- Translations provide students with a better understanding of the test content only fail to reveal the full extent of students' English-language needs
- A translated test may evaluate students' intellectual capabilities but cannot measure students' performance of specific skills
- Translations alter the language of a test but cannot eliminate cultural differences and discrepancies caused by translations
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because, although the assessment is in the ELLs' L1, a direct translation does non accost cultural differences and, every bit a result, the assessment is non completely accessible to ELLs, which volition yield inaccurate results. Options A, B and C are incorrect because a translated exam in the ELLs' native language does non increment the validity or reliability of the test (choice A), give students a ameliorate understanding of the test content (choice B) or evaluate students' intellectual capabilities (selection C). Therefore, the reasons listed do non explain why direct translations yield inaccurate results.
8. A centre schoolhouse bilingual instructor regularly includes news and mag articles in the curriculum that focus on multinational organizations or businesses that highlight careers in which it is advantageous or essential to have knowledge of more than ane language. A primary benefit of using such reading materials for English-language learners (ELLs) is that they permit ELLs to
- place the features of different types of bilingual communities and networks.
- recognize the benefits of existence bilingual and bicultural in a global society.
- promote agreement of the circumstances that may have brought their families to the United States.
- decide where they would like to alive and work when they grow up.
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because the teacher is exposing the students to the importance of being bilingual in a corporate globe through news articles and magazines. Options A, C and D are incorrect because the articles may not necessarily provide information about bilingual communities and networks (selection A), the circumstances that may have brought their families to the United States (option C) and where they would like to live and piece of work when they grow upwards (option D). Therefore, the reasons listed do non describe the benefit of using the described reading materials.
9. Ms. Liang's lesson plans for her tertiary-grade classroom include native linguistic communication (L1) support for academic concepts, including vocabulary development and a bones interaction with new ideas. She wants to ensure that the English-language learners (ELLs) understand the lessons they will exist studying in the upcoming week, specially since nigh of the pedagogy is in English (L2). She continues to emphasize L2 language development throughout the day, but uses L1 to ensure that the ELLs do not fall behind in subject area matter studies as they become more than competent in L2. Ms. Liang's planning indicates that she is working in which of the following special language programs?
- Self-contained English as a Second Linguistic communication (ESL)
- Shared-teaching bilingual
- Transitional or early-go out bilingual
- Two-way bilingual or dual immersion
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option C is correct considering a transitional or early on-get out bilingual program emphasizes L2 evolution; still, the use of L1 ensures students will not fall behind when introducing bookish concepts. Selection A is incorrect because ESL programs involve monolingual English language instruction. Option B is incorrect because the scenario does non mention a shared teaching setup which involves two teachers. Option D is incorrect considering dual immersion involves students from ii unlike language groups which is not described in the scenario.
Competency 002—The kickoff Bilingual Education teacher understands processes of commencement- and 2nd-language acquisition and evolution and applies this knowledge to promote students' language proficiency in their get-go language (L1) and second language (L2).
ten. A 3rd-grade bilingual teacher, Mr. Rivas, reads aloud a procedure for a educatee scientific discipline investigation. After reading aloud the process, he notices that the students are confused about how to begin their investigation. Mr. Rivas then decides to repeat the process step-by-step, modifying the language used in the written instructions so that it is more comprehensible to the students. Which of the following does Mr. Rivas best demonstrate by modifying the lesson?
- Scaffolding instructional technique
- Reciprocal teaching instructional technique
- Sheltered English instructional strategy
- Concept attainment instructional strategy
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Reply expanded
- Selection C is correct considering sheltered English language instruction involves the modification and simplification of complex English structures in order for the language to be comprehensible for ELLs. Option A is wrong because the teacher modifies the linguistic communication used in the written directions, but does non assistance the students to complete the investigation. Option B is incorrect because the scenario does not illustrate a dialogue between teachers and students for the purpose of jointly constructing the meaning of text. Choice D is incorrect considering the scenario does not reverberate students using categorization techniques to ameliorate understand concepts previously presented by the instructor.
11. Which of the following tasks would require the greatest utilize of basic interpersonal communication skills (BICS)?
- Completing an individual science fair projection
- Request for directions to a location
- Using a computer to construct a bar graph
- Listening to a recorded class lecture
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Reply expanded
- Choice B is right because asking for directions involves orally communicating with another person using communication skills. Options A, C and D are wrong considering completing an academic projection (option A), using the reckoner (pick C) and listening to a recorded lecture (option D) are tasks that require the use of cerebral academic language which is Cerebral Academic Linguistic communication Proficiency (CALP).
12. In contrast to an adult learner, an elementary pupil learning the structure of a second language is more likely to
- depend on written representation of the second language.
- apply the structure of the second language spontaneously.
- memorize the grammatical rules of the 2nd language.
- compare the structures of the native and second languages consciously.
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Respond expanded
- Selection B is right because elementary students are less cocky-conscious or aware of making mistakes and, therefore, will attempt speaking the second language more oft than adult learners. Choice A is incorrect considering elementary students will not depend on written representation since their written ability is more express than an adult's. Options C and D are wrong because memorization of grammatical rules and consciously comparison the structure of the native and 2d languages are typical learning behaviors of adult learners, not unproblematic age students.
13. During a social studies lesson, Mr. Donelli instructs the students in the class, including English-language learners (ELLs), to draw pictures that represent the significant of vocabulary words they run into during the lesson. Then he asks them to describe and explain the meaning of the pictures in pairs or small groups. Which of the following statements all-time reflects Mr. Donelli'southward awareness of enquiry-based 2d-language pedagogy for ELLs?
- Exposure to various meaningful linguistic contexts is needed for 2d-linguistic communication acquisition
- Indirect didactics of content cognition maximizes students' second-linguistic communication learning
- Formal educational activity of language structures best fosters the evolution and acquisition of a second language
- Systematic and explicit instruction on language features best develops cognitive abilities in students' second language
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because sketching and discussing academic language equally demonstrated by the teacher are research-based ways of making the text meaningful to the students. Option B is incorrect because explicit educational activity, not indirect instruction, is advisable for ELLs in content education. Pick C is wrong considering formal teaching of language structure such equally grammar and spelling rules are not demonstrated in the scenario, nor is this the best manner for ELLs to acquire a 2nd language. Option D is incorrect because there is no instruction on language features occurring in the scenario.
14. Later on Ms. Pua, a fifth-grade bilingual teacher, distributes an informative article in English to her form, one pupil says, "Instructor, the word 'coast' sounds like the Spanish give-and-take costa." Earlier the course reads the article, Ms. Pua arranges the students in small groups and asks them to find and discuss the meaning of words that sound alike in English (L2) and Spanish (L1). And so she creates a chart to tape each group's findings. The activity best illustrates Ms. Pua'southward understanding that
- analyzing word parts such as root words and affixes facilitates acquisition and application of content knowledge.
- providing high-interest reading selections motivates students to feel comfy reading in L2.
- making connections between the students' L1 and L2 helps build vocabulary noesis and supports reading comprehension.
- modeling metacognitive strategies for students helps students utilize the strategies in L1 and L2 activities.
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Pick C is correct because the teacher is having students build prior knowledge of a reading pick past identifying a correlation in an L1 cognate, in guild to develop L2 vocabulary and text comprehension. Option A is incorrect because the students are identifying cognates and not analyzing give-and-take parts such equally root words and affixes. Selection B is incorrect because the scenario does non show the teacher specifically choosing high interest text. Selection D is incorrect because the instructor is not demonstrating a learning process or metacognition.
15. A bones assumption underlying dual-language curriculum development and instruction is that students develop a get-go language through
- imitation, reproducing language through approximate imitation of what they hear.
- syntax, discovering the organizing principles of the language they are being exposed to.
- hypothesis testing, finding rules in their language and testing them by applying the rules they accept formulated.
- linguistic communication acquisition, developing grammer based on the linguistic input they receive.
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because students acquire first language primarily by finding rules in the language and testing the rules by applying them. The dual language curriculum is designed then students test what they know in their L1 and use information technology to L2. Choice A is incorrect because the dual language curriculum is designed so students make connections across L1 and L2. If curriculum was developed purely through imitation, students would not take language risks in L2 to apply rules they know in L1. Options B and D are wrong because they merely focus on syntax and grammar, and students make sense of semantic and pragmatic systems of language as well.
16. During a guided reading lesson, Lisbeth, a second-grade English-linguistic communication learner whose native linguistic communication is Spanish, stumbles over the word "eating house." Her teacher reminds her to think virtually what is happening in the story and suggests that she think of the give-and-take in Spanish, which is a cognate. Afterwards, Lisbeth successfully reads the word in English language and continues reading the remainder of the text. In the scenario, the instructor encouraged Lisbeth to use her noesis of her native language primarily to
- facilitate comprehension.
- increase educatee confidence.
- develop structural analysis.
- focus on context clues.
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse respond. Answer expanded
- Choice A is correct because Lisbeth is applying her knowledge of a cognate of the English word "restaurant" so that she tin can better encompass her reading consignment in English. Option B is incorrect considering the use of Castilian increases her comprehension, but may not increase conviction in reading; this is a secondary effect. Selection C is wrong because she is not analyzing the word parts to understand the pregnant every bit applicable in structural analysis. Option D is incorrect because she is not using the surrounding text to comprehend unfamiliar words.
Apply the chart to answer the question that follows.
The chart depicts the stages of linguistic communication acquisition for English-language learners (ELLs).

The chart has 5 horizontal boxes with an pointer inbetween each of them. The lodge is as follows: preproduction, production, emergence, fluency, fluency.
17. A teacher is facilitating a reading-comprehension activity to arm-twist information virtually a story the students merely read. Which of the following would exist the most appropriate question for the teacher to ask ELLs in the early on production phase?
- "Why did the graphic symbol evolve?"
- "Where did yous find the answer?"
- "Was it a whale or a dolphin?"
- "What do you lot think volition happen side by side?"
- Enter to expand or plummet reply. Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because students in the early production stage are nigh successful when they can select from a choice provided past the teacher. Options A and B are incorrect because these questions would be more than appropriate for students at the speech emergence level because they tin can produce simple sentences. Option D is incorrect because this question is most advisable for students at the intermediate fluency level who can explain with more details.
18. Later on iv months in the United states of america, Sal, a 5th grader, still rarely speaks in English (L2) in his bilingual course. In fact, he rarely speaks at all except in short sentences in his first linguistic communication (L1) during one-on-one interactions with his instructor. The teacher has discussed the situation with Sal's parents, who seem unconcerned and clinch that Sal is also very quiet at home. Which of the following is the most advisable step the teacher should take side by side regarding Sal?
- Calling on Sal periodically during grade discussions to provide him with an accurate context for speaking in front end of his peers in L1 or English (L2)
- Continuing to monitor Sal's progress and acknowledging that there may be personal factors influencing his linguistic communication performance in L1 and L2
- Initiating L2 instruction with Sal that includes activities that require the employ of L2 oral linguistic communication
- Regularly placing Sal in situations in which he must speak L1 and L2 in guild to take part in activities he enjoys
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option B is correct considering students' achievement of a 2d language varies from student to student. A student'south personal bug too play a role in development of a 2nd language. Therefore, the teacher monitoring the educatee is the best answer. Options A, C and D are incorrect because calling on the student periodically (option A), initiating English education (pick C) and creating situations in which he must speak in L1 and L2 (pick D) will all raise Sal's affective filter; therefore, these options will decrease his ability to learn and/or develop his language in L1 or L2.
19. The post-obit chart depicts the stages of language acquisition for ELLs.

The chart has v horizontal boxes with an arrow inbetween each of them. The order is as follows: preproduction, production, emergence, fluency, fluency.
Which of the following adaptations to the vocabulary map activeness is the most appropriate for an ELL who is functioning at the preproduction stage of language development?
- Modeling and explicitly correcting the ELL's pronunciation of selected vocabulary words for the word map
- Expanding on the ELL's word map by calculation adjectives
- Exposing the ELL to boosted words that will be added to the word map
- Helping the ELL select the vocabulary words for the word map
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Reply expanded
- Option D is right because in helping select the vocabulary words for the word map, the teacher will select words that are appropriate for students at the preproduction stage. The instructor can select words that are true cognates in the ELL's primary language which will help the ELLs complete the assignment. Choice A is incorrect considering explicitly correcting pronunciation raises ELL's affective filter. Options B and C are incorrect considering calculation adjectives (option B) and additional words (option C) are besides advanced for an ELL at the preproduction.
Competency 003—The beginning Bilingual Education teacher has comprehensive knowledge of the development and assessment of literacy in L1 and the evolution and assessment of biliteracy.
twenty. Which of the post-obit would best help English language-linguistic communication learners in a bilingual grade improve their decoding of words with long and short/i/ vowel sounds in English (L2)?
- Reviewing how the letter of the alphabet/i/ sounds in the students' commencement linguistic communication (L1), so educational activity the sounds of the letter /i/ in L2
- Having the students study the rules of how the long and short vowels can be spelled in L2
- Comparing the rules of how the long and short vowels can exist spelled in the students' L1 and L2
- Developing visual cues that testify students when words have the long or brusque/i/ sound in L2
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option A is correct considering ELLs will have greater success in decoding words with long and short "i" vowel sounds when they brand the connection to the vowel audio they know in L1. Options B and D are wrong because studying the rules for spelling long and short vowel sounds in L2 (option B) and developing visual cues for long or curt "i" vowel sounds in L2 (option D) practice not help students connect their prior noesis of the "i" vowel sound from their L1. Option C is wrong because, although students are connecting their spelling knowledge of L1 and L2, they are not connecting the sounds from L1 to L2; therefore, ELLs will nonetheless struggle with decoding long and brusk "i" vowel sounds.
21. Mr. Ramirez uses portfolio assessments with a loftier school scientific discipline class that includes English-language learners (ELLs). Portfolios are peculiarly appropriate for ELLs because they are used to
- guide teacher instruction based on standards not covered.
- evaluate students and decide whether reteaching of content is necessary.
- testify the students their weaknesses in their English-language proficiency development.
- demonstrate student growth over time through the use of multiple indicators.
- Enter to expand or collapse reply. Respond expanded
- Option D is right considering portfolios are used to demonstrate pupil growth more fully through the utilize of multiple indicators. Options A, B and C are incorrect because portfolios are not used to guide teacher teaching based on standards not covered (option A), to reteach of content (portfolios are the final products) (choice B) or used to showcase students' weaknesses (selection C).
22. A kindergarten bilingual teacher wants to develop English-language learners' (ELLs) phonemic awareness skills in their commencement linguistic communication (L1), which is an alphabetic language. Which of the following literacy activities would be most effective to use for the teacher'due south purpose?
- Singing the alphabet song in L1 to ELLs while pointing to each letter on an L1 alphabet nautical chart
- Educational activity ELLs to distinguish between pictures and impress in books in L1 and ecology print
- Playing rhyming games with ELLs in L1 and orally retelling stories that feature rhyming words in L1
- Teaching ELLs alphabet games in L1 that involve recognizing and writing private messages in L1
- Enter to aggrandize or plummet respond. Answer expanded
- Option C is correct considering phonemic sensation involves orally producing or manipulating letter of the alphabet sounds such as rhyming words. Options A, B and D are incorrect because pointing to the alphabet chart while singing the alphabet (option A), distinguishing between pictures and print in books (option B) and playing games to recognize and write letters (option D) all incorporate print and phonics; therefore, they are not related to phonemic awareness.
23. In a high school social studies grade, students are required to complete daily dialogue journals based on reading passages. A primary benefit of dialogue journal writing for English-language learners is that they
- are instructed on the conventions of standard written language based on the errors plant in their journal writing.
- are provided with opportunities to amend their reading and writing skills by reading aloud their dialogue journals.
- can receive more than accurate grades on the writing abilities shown in their dialogue journals.
- can take more risks in expressing their thoughts through periodical writing than they can through oral expression.
- Enter to expand or plummet respond. Answer expanded
- Option D is correct because journals provide a condom and individual identify to write, allowing ELLs a identify to have risks that are necessary for them to take to develop fluency in their writing. Option A is incorrect considering, while a instructor may analyze the journal entry for language errors, the focus of dialogue journals is fluency. Students may exist aware of the appropriate conventions but are not applying them in this type of writing. Option B is wrong considering dialogue journals are not meant to be shared with classmates; in fact, sharing them with classmates will likely raise their affective filter. Option C is incorrect because the dialogue journals are not meant to be formally assessed.
24. A middle school instructor uses the following give-and-take-generation activity for a class that includes English-linguistic communication learners (ELLs). The teacher writes the word "scribe" on the board and prompts the students to begin all the words they tin think of that contain "scribe." The post-obit are some of the students' words.
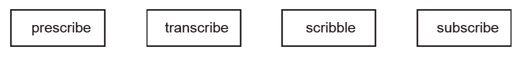
There are four boxes of equal length and size in a horizontal line. Each box has a discussion written in the center of information technology. The club of the words are as follows: prescribe, transcribe, scribble, subscribe.
The instructor then asks the students to examine each give-and-take carefully and figure out what words containing "scribe" might hateful by orally creating sentences that employ the words. The form determines that "scribe" means "to write." The teacher then revisits each word with the class to meet if the meaning matches. The activeness best helps the ELLs develop vocabulary by
- categorizing new content vocabulary into groups predetermined by the teacher.
- comprehending new content vocabulary through assay.
- taking linguistic communication risks in a rich language environment.
- self-selecting new vocabulary that is essential to understanding content-specific concepts.
- Enter to expand or collapse reply. Answer expanded
- Option B is right because ELLs examine each word and, through analysis, determine that scribe means "to write." Option A is incorrect because students are not categorizing the words. Likewise, they brainstormed the words, non the teacher. Option C is incorrect because there is no evidence of risk taking in the scenario. Option D is incorrect because there is no evidence of the vocabulary words beingness content specific in the scenario; rather, students are asked to begin words that follow a pattern.
25. A primary difference betwixt English and Spanish literacy skill development is that Spanish literacy involves
- the manipulation of individual phonemes within words.
- several sounds associated with ane vowel.
- an emphasis on using individual syllables.
- the product of onsets and rimes.
- Enter to expand or plummet reply. Reply expanded
- Option C is correct because Spanish language has a well-defined syllabic construction that depends on the syllable for literacy development. Selection A is wrong because phonemes can be isolated in Castilian, merely it is rarely done and non part of literacy teaching. Option B is incorrect because vowels each have 1 audio in Castilian. Option D is wrong considering identifying and producing onsets and rimes can be washed in Spanish, but literacy educational activity does not begin with onsets and rimes; rather it begins with the written report of the syllabic structure.
Use the graphic below to answer the question that follows.
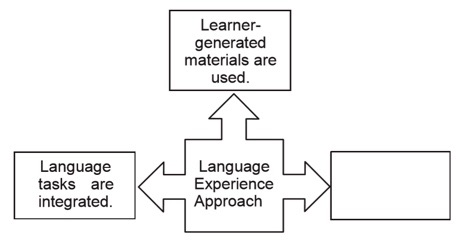
At that place are 2 levels of this diagram. The diagram begins with 3 boxes on the showtime or bottom layer, with the middle box being the starting betoken, which has a label of "Language Experience Arroyo" and has 3 arrows coming out of the left, superlative, and correct sides of information technology's outline. The left arrow is pointing to a box that has a label of "Language tasks are integrated". The elevation pointer is pointing to a box that has a label of "Learner-generated materials are used". And the right arrow is pointing to a box that is bare, or has no label.
26. Which of the following is an attribute of the linguistic communication experience approach that correctly completes the graphic?
- Lessons are most suitable for utilize with avant-garde-level language learners
- Learners determine the difficulty level of the vocabulary and grammar
- Lessons progress from unknown contexts to familiar contexts
- Learners facilitate whole-group discussions
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Respond expanded
- Option B is correct because in the language experience approach, the learner describes his or her experience and, therefore, determines the vocabulary and grammar. Option A is incorrect because the approach is actually suitable for all language learners. Option C is incorrect because the lesson begins with the students' experiences; therefore, the context is known, not unknown. Option D is incorrect because the teachers lead and stimulate discussions.
27. Which of the following is true according to Cummins' common underlying proficiency (CUP) section of the "dual-iceberg" model in relation to English-language learners' (ELLs) first (L1) and second language (L2)?
- ELLs take difficulty transferring content knowledge from L1 to L2
- ELLs have cognitive academic skills that are readily used in both L1 and L2
- ELLs' previous schooling in L1 has little to no effect on bookish performance in L2
- ELLs show success in L2 bookish tasks just when they accept mastered bones interpersonal communication skills in L1
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Reply expanded
- Option B is correct because co-ordinate to Cummins, the two languages used by a bilingual pupil announced to exist separate on the surface, but in reality, the student is operating under 1 system for both languages. Hence, what a student knows in one language can be readily applied to another linguistic communication. Option A is incorrect because, according to Cummins, students can transfer the content cognition from L1 to L2. Selection C is incorrect because CUP doesn't take academic functioning into account. Option D is incorrect because BICS are not related to Cummins theory.
28. The Texas Teaching Agency has adopted language-level descriptors and expectations for English language-language learners to replace the English as a 2d Linguistic communication (ESL) standards. School districts are required to implement these expectations equally an integral function of the curriculum across all content areas and content teachers should use the standards to guide educational activity. The expectations are known as the
- Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS).
- English Language Proficiency Standards (ELPS).
- Texas English Language Proficiency Cess Organization (TELPAS).
- Particularly Designed Academic Education in English (SDAIE).
- Enter to expand or collapse respond. Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because the English Language Proficiency Standards (ELPS) are the state curriculum for English-language learners to be used alongside the TEKS in all content areas, not merely in bilingual or ESL classrooms. Option A is incorrect because the TEKS are the state curriculum for all students. Pick C is incorrect because the TELPAS measures the bookish progress of Limited English Proficient (LEP) students. Option D is incorrect considering the SDAIE is a didactics approach, non linguistic communication descriptors or expectations.
Competency 004—The beginning Bilingual Didactics teacher has comprehensive knowledge of content area pedagogy in L1 and L2 and uses this cognition to promote bilingual students' bookish accomplishment beyond the curriculum.
29. Mr. Lopez teaches at a dual-language immersion school in which science classes are taught in English. An English-linguistic communication learner in the class, Raisha, currently functions at a beginning level of English proficiency. To best assist Raisha'due south comprehension during teaching, Mr. Lopez should
- provide her with graphic organizers to employ when taking notes or communicating ideas.
- assign her a peer tutor to simultaneously interpret the class lectures.
- straight her to express ideas in her native language until she masters the unit of measurement concepts.
- instruct her to write a summary of critical concepts at the end of each lesson.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Reply expanded
- Choice A is correct because the graphic organizer would best increase the comprehensible input of the lesson. Choice B is incorrect considering asking some other student to interpret a lesson simultaneously is not all-time exercise and it wouldn't help develop Raisha'south English comprehension. Choice C is incorrect because asking her to use her native language to express her ideas wouldn't increment her comprehension of the lesson. Option D is wrong because writing a summary is an assessment for a student at the intermediate level of English proficiency, not first level.
30. The following daily instructional objective is posted on the board of a science class.
Content Objective: Students will interpret data relative to moving objects and produce a motion graph.
Which of the following additional pieces of information would the instructor need to mail service alongside the content objective in guild to run into the criteria of sheltered instruction?
- A description of the cooperative learning action students will engage in as office of the content objective
- A list of vocabulary words that students will acquire or review during the lesson
- A language objective that will be used to focus on developing student vocabulary
- A description in the lesson program of how the teacher will alter linguistic communication to increase student comprehension
- Enter to aggrandize or plummet answer. Answer expanded
- Choice C is right because language objectives are an essential and explicit component of sheltered educational activity and must be included to meet the criteria of sheltered instruction. Options A, B and D are incorrect because while including cooperative learning activities (option A), lists of vocabulary words that students will learn (option B) and descriptions of modifications (pick D) are all helpful for instruction and planning, they are non essential to run across the criteria of sheltered instruction.
31. English-language learners (ELLs) in a second-form class are starting time an interdisciplinary unit about plants. To help the ELLs monitor their own learning during the unit of measurement, it would exist most effective for the teacher to
- provide them with a checklist of all the activities in the unit and encourage them to mark off each activity every bit it is completed.
- encourage them to go on all of their unit work in a folder and keep a record of each course or teacher comment on the inside encompass.
- help them develop a learning log in which they write what they know near plants and and then verify their understandings throughout the unit.
- teach them how to utilise reference materials most plants and then encourage them to correct their own errors on unit of measurement work.
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Selection C is correct because students are practicing an important self-monitoring skill by first recording their assertions of what they know then edifice upon their personal understandings based on their work in the unit. Personal reflection is an important self- monitoring skill. Options A and B are incorrect considering while completing checklists and keeping work in a folder are excellent ways to ensure completion and organization of work, they exercise not ensure that ELLs are cocky-monitoring their learning. Choice D is incorrect because having students correct their work based on reference materials is non a way for students to monitor their learning; rather, it is a fashion for them to ostend facts.
32. Mr. Ullah, a bilingual instructor, helps English language-language learners (ELLs) brand a listing of questions to guide and meliorate their writing. He then encourages them to develop the habit of referring to the questions during the writing process. The following are some examples of the questions.

Mr. Ullah'due south approach is benefitting the ELLs primarily past developing their ability to
- work independently to amend their writing skills.
- adjust the reading level of their finished written piece of work.
- appraise their writing progress over the course of the year.
- self-correct their written mistakes.
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option A is right because answering the questions will probable provide ELLs with ways to ensure that their writing is articulate and targeting the right audition. Options B, C and D are incorrect because the questions are not associated with adjustment of reading level (option B), assessing writing progress over time (option C) or correct writing conventions (choice D).
33. Which of the following social studies activities would exist most appropriate for English-language learners who are reading and speaking at the intermediate linguistic communication proficiency level in English?
- Cartoon private family unit portraits and naming the people in them
- Participating in a guided discussion nigh customs helpers and reading a passage about them
- Creating a model of a neighborhood out of pocket-sized paper-thin boxes with labels identifying a schoolhouse, a town hall and other community buildings
- Making a collage from magazine pictures of various forms of transportation and reading passages nearly them
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option B is correct because ELLs at the intermediate level of reading and speaking can participate in a guided discussion and comprehend a passage nearly community workers. Both of these activities would assistance develop ELLs reading and speaking skills. Options A, C and D are wrong because creating drawings and naming the people in them (option A), creating models with labels (option C) and making collages and reading passages nigh them (selection D) do non help develop the ELLs' skills in reading and speaking.
34. English-language learners (ELLs) are practicing coin calculations in mathematics lessons in their principal language and learning nutrient names in English-arts lessons. Which of the following activities would all-time integrate the ELLs' English language- arts evolution with their content-surface area development?
- The ELLs make a listing in English of foods they would similar to purchase and use a price list to make up one's mind how much of each type of food they tin buy with ten dollars
- The teacher takes the ELLs on a field trip to a supermarket and has them fill in the prices of several unlike foods on a checklist written in English
- The ELLs search through English supermarket flyers to cutting out advertisements and create a visual display of the foods they like best and their prices
- The teacher creates worksheets with story bug written in English in which the ELLs must decide the totals and right change owed for various food purchases
- Enter to expand or plummet reply. Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because the teacher is integrating language and content instruction for ELLs. The activeness includes English-language development past listing the foods in English and content-based mathematics objectives with money calculations. Options B, C and D are incorrect because, while filling in price lists (option B), cutting out supermarket flyers with prices (choice C) and answering story bug related to nutrient purchases (option D) are good activities related to food and money, they each lack an chemical element to appropriately integrate both language arts and mathematics content-area development.
35. A social studies course, including English language-language learners (ELLs) at varying levels of English language-language proficiency, is analyzing the reasons for the colonization of Northward America. The lesson plan states that students volition read the colonization of Due north America sections in their social studies text and independently complete a time line detailing the establishment of the xiii colonies. Which of the following instructional activities is nearly beneficial in helping ELLs build background cognition prior to the assignment?
- The teacher presents a slide testify that depicts critical events and life in the colonies
- Students create dioramas that depict critical events in establishing the colonies and share them with the class
- The instructor provides students with a brief lecture of the colonies supplemented with maps
- Students piece of work in cooperative groups to complete a concept map detailing what they already know most the colonies
- Enter to aggrandize or plummet respond. Answer expanded
- Selection A is correct because the visual of the slides of the critical events volition specifically help ELLs at all linguistic communication proficiency levels comprehend the details of the institution of the colonies. Pick B is incorrect because students can create dioramas in one case they have background noesis, but not prior to understanding and/or having knowledge of the colonies. Option C is wrong because non all levels of ELLs would comprehend the details of the institution of the colonies in a brief lecture. The map would give them a visual of the colonies but volition not provide them the details of their establishment. Option D is incorrect because the concept map assesses what ELLs already know about the colonies; it doesn't provide them with background knowledge.
36. Students can most effectively reinforce their conquering of a new vocabulary give-and-take by doing which of the following?
- Studying the etymology of the new discussion
- Identifying the part of speech of the new give-and-take
- Using various forms of the new word in sentences
- Locating several synonyms of the new discussion in a thesaurus
- Enter to aggrandize or collapse respond. Answer expanded
- Option C is correct because students are using the new word in sentences, which helps students apply their understanding of the give-and-take; application leads to eventual acquisition of the word. Options A, B and D are incorrect because, while learning the etymology of a new word (option A), identifying the word's part of speech (pick B) and locating synonyms of the discussion (pick D) volition provide more data, they do not require students to use the word which best promotes acquisition.
37. English language-language learners (ELLs) volition be working in cooperative-learning groups to complete an cease of a unit of measurement content-area project in English. Before the ELLs meet for the outset time with their grouping, the teacher asks them to jot down in English everything they know about the project's topic. Afterward, they meet with their grouping with their paper in hand to use equally a reference. The annotation-taking activity helps the ELLs work more than effectively with the content primarily because it
- prepares them to talk over the content in English.
- allows them to lower their affective filter.
- provides a preview of the content vocabulary in English.
- incorporates authentic language use.
- Enter to expand or plummet answer. Answer expanded
- Option A is correct considering the note-taking activity primarily helps activate ELLs' content knowledge from the unit. They will exist prepared to discuss what they know in their groups because they are writing downwardly what they know almost the topic using their noesis of the unit. Option B is incorrect because ELLs are not consciously enlightened of their affective filter. The ELLs affective filter will be lowered because they are able to discuss the content, but lowering the affective filter is not the primary purpose of the note-taking activity. Option C is incorrect considering the ELLs are not previewing vocabulary if they write downward vocabulary that is from their knowledge of the unit. Previewing vocabulary is done before units of study to increase comprehensible input. Option D is incorrect because the note-taking activity is non primarily using language authentically; the discussion in their small groups allows students to use linguistic communication in a more authentic manner.
Multiple-Competencies Passages
Questions 38–40 refer to the following information.
Ms. Rodriguez uses a diverseness of discussion maps to introduce and expand students' content vocabulary in her 5th-grade social studies class, which includes varying levels of English-language learners (ELLs). The pupil objectives during the vocabulary activity are listed below.
Content objective: Students will identify and analyze new vocabulary words.
Linguistic communication objective: Students will explicate the new vocabulary words in groups.
She begins by organizing the students into heterogeneous report groups and assigning each group a prereading activity to exist used with the social studies textbook. Equally they read in their groups, the students must create a listing of target words to define and after discuss as a group.
Every bit a follow-up activity, Ms. Rodriguez has the students complete vocabulary maps with the targeted words equally illustrated beneath. Finally, the students share their maps with the whole class.
The following is an case of a word map completed past an ELL.

Competency 004—The beginning Bilingual Education teacher has comprehensive knowledge of content area educational activity in L1 and L2 and uses this knowledge to promote bilingual students' academic accomplishment across the curriculum.
38. Which of the following function of the word map is most likely to help the ELLs internalize the new vocabulary word?
- Role 2
- Part three
- Role iv
- Part 6
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option D is right because internalizing the vocabulary words will almost likely happen during Step 6 in which students make a personal connection to the new give-and-take past using the discussion in a judgement. Options A, B and C are wrong considering writing a definition (choice A), synonym (selection B) and antonym (option C) of the give-and-take might provide groundwork; still, the activities do not help students internalize and utilise the new discussion.
39. The collaborative activity Ms. Rodriguez assigned is fulfilling the language objective primarily because it gives the ELLs the opportunity to
- collaborate socially with their classmates.
- experience motivation that comes with working in teams.
- practice English language as a means of expressing their ideas.
- assess their own English proficiency equally compared with that of their peers.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option C is correct considering the collaborative activeness involves choosing the words to discuss, which involves expressing their ideas about the new vocabulary which reflects the linguistic communication objective. Pick A is wrong considering students are interacting well-nigh instructional content, not socially. Choice B is incorrect because the goal for the collaboration is non to increase motivation; the goal is to provide an opportunity for give-and-take. Option D is incorrect because students are not evaluating their proficiency levels in the collaborative piece of work, nor is this an appropriate task for students.
Competency 002—The kickoff Bilingual Education teacher understands processes of beginning- and second-language acquisition and development and applies this knowledge to promote students' language proficiency in their first language (L1) and second language (L2).
40. The word map used in this lesson best helps ELLs to develop their vocabulary skills through
- identifying relationships betwixt newly learned words and familiar words.
- applying effective prereading strategies in scanning an unfamiliar text.
- facilitating translation of texts into their native languages.
- using mnemonic devices that link give-and-take forms to their meanings.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Option A is correct because the give-and-take map allows students to discern similarities and differences amongst words and create links to known words in their primary linguistic communication. Option B is wrong because word maps are non part of scanning unfamiliar texts. Option C is wrong because students are non participating in any translation activities. Option D is wrong because students are not applying retention-based mnemonic devices in the give-and-take-map activity.
varnermannery1952.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.tx.nesinc.com/Content/StudyGuide/TX_SG_SRI_164.htm
0 Response to "A Third Grade Teacher Is Creating a Language Arts Lesson to Address the Following Standard"
Postar um comentário